Public Transit + DRL
Real-time Route Task Assignment for Cost-effective Tram Operation with Deep Reinforcement Learning @PolyU, Hong Kong
In modern cities, some public transit systems, e.g. trams and buses, face some uncertainties in their operation, such as disruption and bunching. This leads to inefficient service to the public and seriously affects the working hours and welfare of motormen, which further upsurges the operating cost of transport company due to service failure and overtime pay. Thus, how to develop a flexible, robust, and efficient real-time online task assignment scheme within urban public transit network according to such complex system dynamics motivates this project.

An example of buses bunching in Hong Kong. (Source: 4TU.ResearchData)
Objectives:
- Create a simulator according to Hong Kong tram network that will allow to test the performance of operational strategies, which will easily extend to other public transit systems.
- Develop a Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) based agent to generate tasks to motormen in real-time assessment of transport status.
- Explore a learning-based approach to alleviate or circumvent the high computational complexity of traditional optimization techniques.
Preview:
- DRL-based control framework of an illustration of tram network with three routes. (Practical case in Hong Kong pls refer to Hong Kong Tramways - Ding Ding)
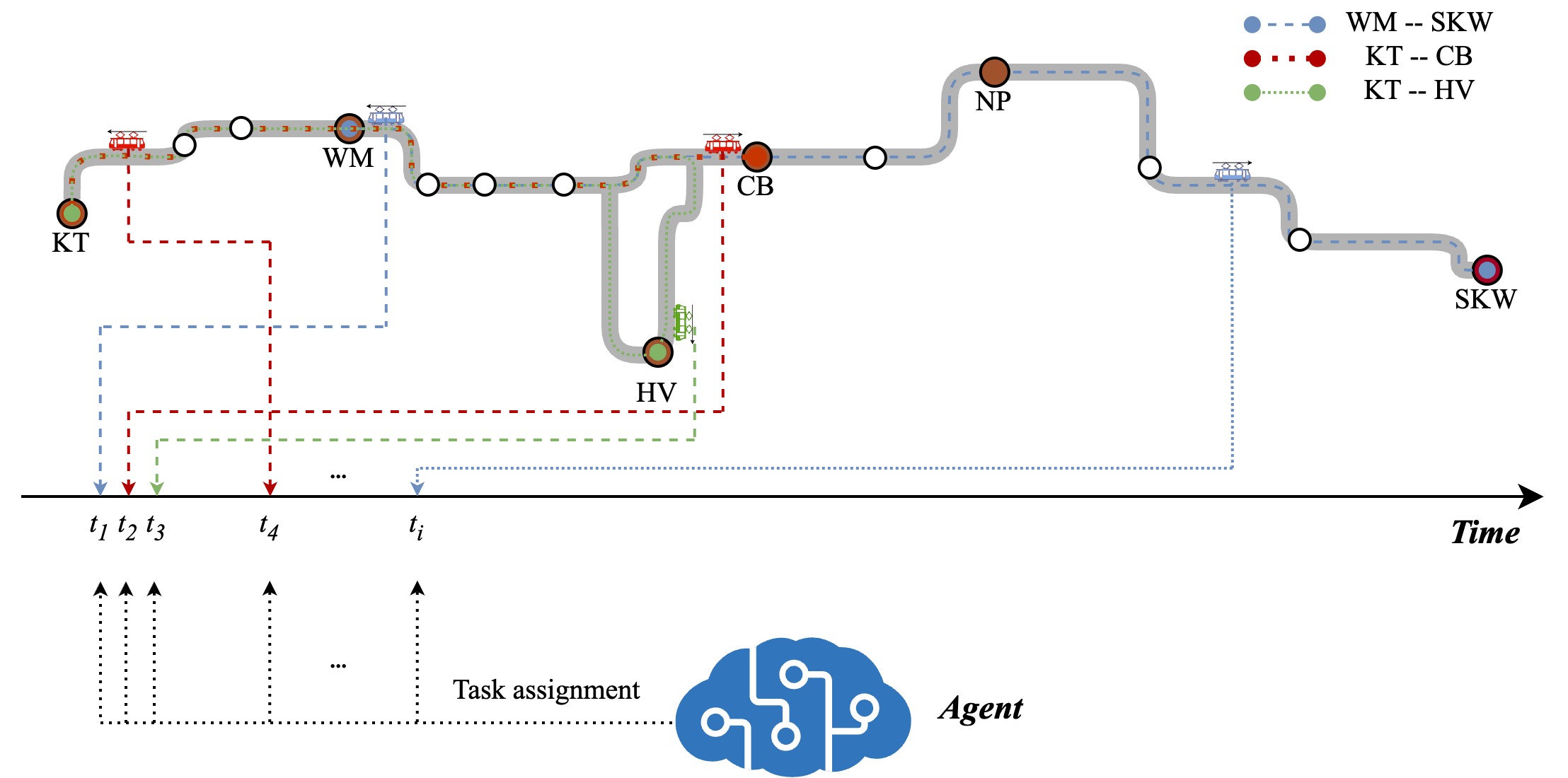
- With a developed DRL-based agent, the experiments show that the agent can have all the motormen take meal breaks and sign off while maintaining a low under-coverage rate on one operational day.

Output: A research report had submitted to the Hong Kong Polytechnic University while the manuscript to a journal is under preparation.
Reference:
- David SW Lai and Janny MY Leung. Real-time rescheduling and disruption management for public transit. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 6(1):17–33, 2018.